加州大学洛杉矶分校的研究人员最近领导的一项研究发现,长期感染 COVID 并出现嗅觉丧失(嗅觉丧失)的人与那些恢复嗅觉或恢复嗅觉的人表现出不同的大脑活动模式从未感染过 COVID-19。 这项观察性研究使用 MRI 扫描,发现长期 COVID-19 嗅觉丧失患者的大脑活动减少,眶额皮质和前额皮质之间的连接受损。 在 COVID 后恢复嗅觉的人中,这种联系没有受到影响。 结果表明,长时间的 COVID-19 嗅觉丧失可能与阻止气味被正确处理的大脑变化有关,但由于它在临床上是可逆的,因此训练嗅觉可能有助于大脑恢复这种感觉。 该研究还发现,因 COVID-19 而长期丧失嗅觉的人的大脑可能会通过加强与其他感觉区域的联系来弥补。
伦敦大学学院 (UCL) 的研究人员领导的一项新研究发现,长期感染 COVID 并经历嗅觉丧失的人在大脑的特定区域表现出不同的活动模式。
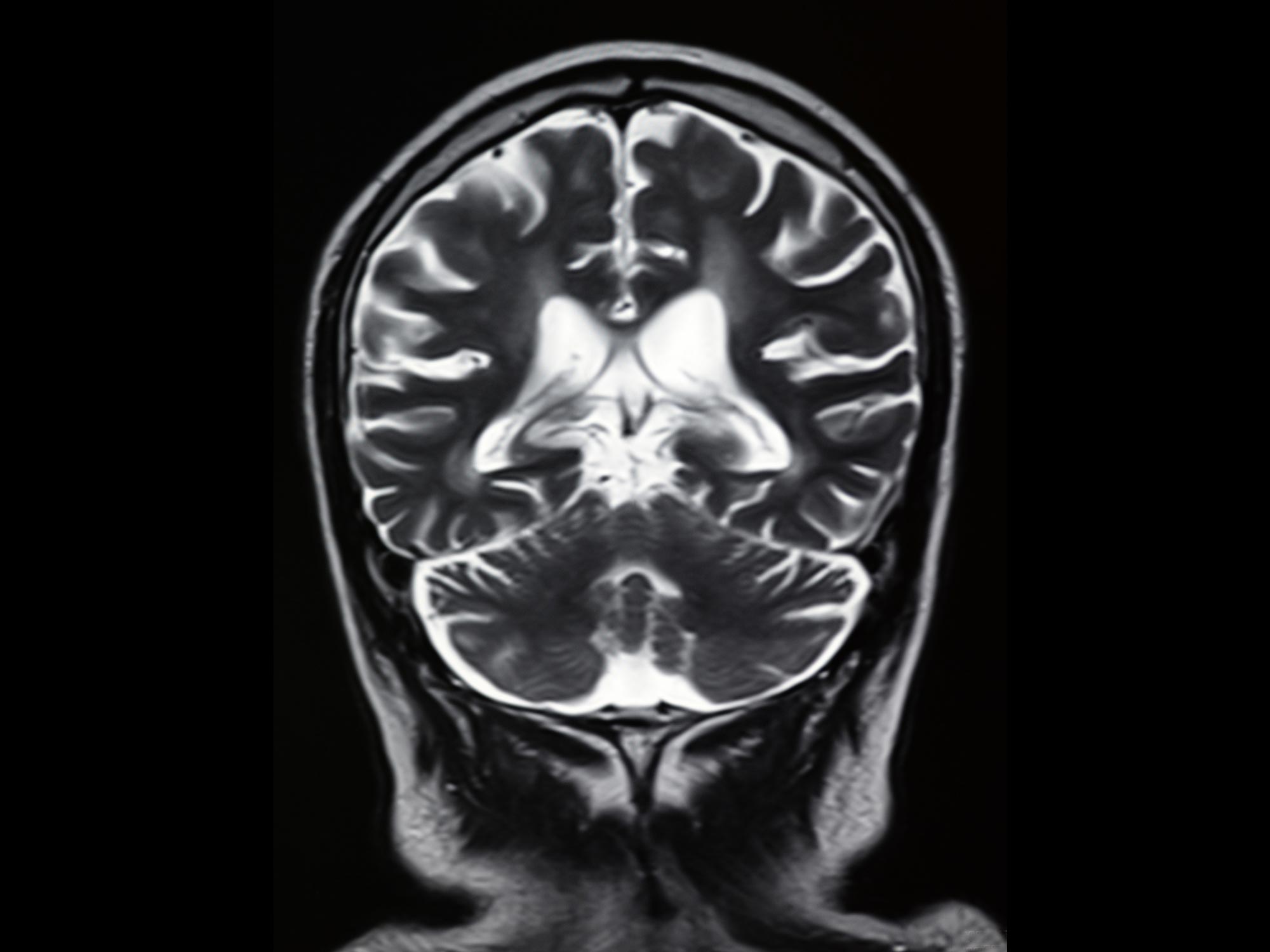
该研究使用核磁共振扫描来比较长时间感染 COVID 并失去嗅觉的人、感染 COVID 后嗅觉恢复正常的人以及从未检测出阳性的人的大脑活动。[{” attribute=””>COVID-19.
Published in the journal eClinicalMedicine, the observational study found that people with long COVID smell loss had reduced brain activity and impaired communication between two parts of the brain that process important smell information: the orbitofrontal cortex and the pre-frontal cortex. This connection was not impaired in people who had regained their sense of smell after COVID.
The findings suggest smell loss, known as anosmia, caused by long COVID is linked to a change in the brain that stops smells from being processed properly. Because it’s clinically reversible, as shown in some subjects, it may be possible to retrain the brain to recover its sense of smell in people suffering the side effects of long COVID.
Dr. Jed Wingrove (UCL Department of Medicine) the lead author of the study, said: “Persistent loss of smell is just one way long COVID is still impacting people’s quality of life – smell is something we take for granted, but it guides us in lots of ways and is closely tied to our overall wellbeing. Our study gives reassurance that, for the majority of people whose sense of smell comes back, there are no permanent changes to brain activity.”
Joint senior author, Professor Claudia Wheeler-Kingshott (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology), said: “Our findings highlight the impact COVID-19 is having on brain function. They raise the intriguing possibility that olfactory training – that is, retraining the brain to process different scents – could help the brain to recover lost pathways, and help people with long COVID recover their sense of smell.”
Researchers say their findings also suggest that the brains of people with long COVID smell loss might be compensating for this lost sense by boosting connections with other sensory regions: their brains had increased activity between the parts of the brain that process smell and areas that process sight (the visual cortex).
“This tells us that the neurons that would normally process smell are still there, but they’re just working in a different way,” said Dr. Wingrove.
Professor Rachel Batterham (UCL Division of Medicine), also joint senior author of the study said: “This is the first study to our knowledge that looks at how brain activity changes in people with long COVID smell loss. It builds on the work we undertook during the first wave of the pandemic, which was one of the first to describe the link between COVID-19 infection with both loss of smell and taste.”
Reference: “Aberrant olfactory network functional connectivity in people with olfactory dysfunction following COVID-19 infection: an exploratory, observational study” by Jed Wingrove, Janine Makaronidis, Ferran Prados, Baris Kanber, Marios C. Yiannakas, Cormac Magee, Gloria Castellazzi, Louis Grandjean, Xavier Golay, Carmen Tur, Olga Ciccarelli, Egidio D’Angelo, Claudia A.M. Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott and Rachel L. Batterham, 2 March 2023, eClinicalMedicine.
DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101883
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).

“社交媒體傳播者。學生。讀者。麻煩製造者。典型的性格內向。”






More Stories
研究发现巨型外星球的密度相当于蓬松的棉花糖
“史无前例”——二氧化碳上升速度比有记录的历史上任何时候都要快十倍
研究发现,气候变化可能与美国人偏头痛严重程度和频率升高有关